- Ethereum’s user activity dropped to 2025 lows, signaling waning demand and potential inflationary pressure.
- With weak on-chain metrics and growing competition, Ethereum’s position as a leading blockchain is questioned.
User activity on the Ethereum [ETH] network is slipping, casting a shadow over demand for the leading Layer-1 blockchain.
Recently, ETH’s daily active addresses and new wallet creations hit their lowest levels in 2025. This decline highlights reduced on-chain engagement.
Ethereum’s falling user metrics raise concerns about its ability to maintain its dominance. Faster and cheaper competitors are intensifying the challenge for Ethereum’s position.
Ethereum’s on-chain metrics sink as network demand dwindles
Ethereum is experiencing a sharp pullback in user activity, with key network indicators falling to their lowest levels so far this year.
On the 16th of March, the number of active addresses participating in ETH transactions dropped to 361,078, the lowest daily count recorded so far this year.
This steep decline highlights weakening on-chain engagement, a metric closely tied to transactional demand and fee generation.
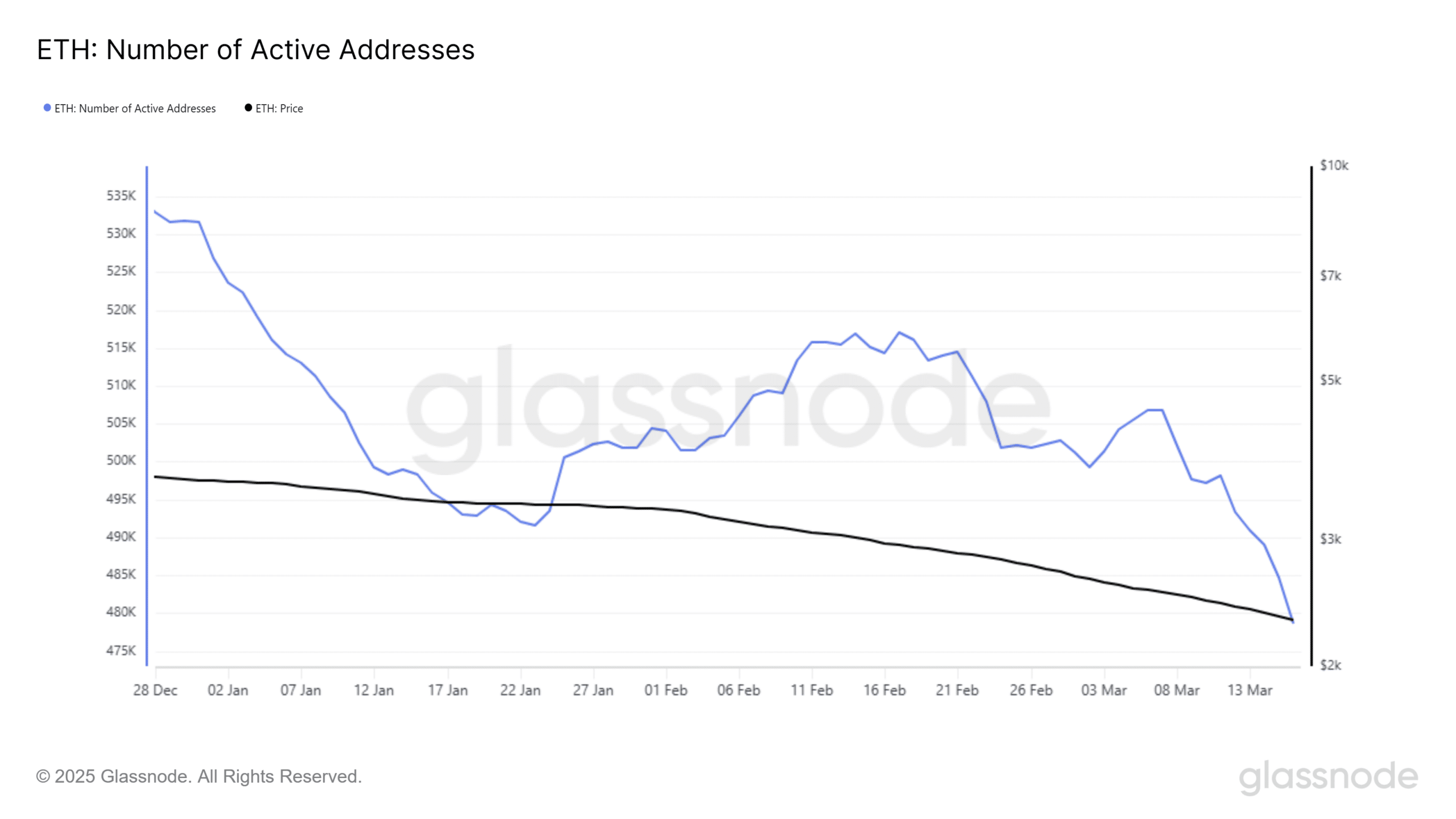
Source: Glassnode
The decline in active usage lowers the amount of ETH burned through gas fees, increasing the asset’s inflationary pressure. A weaker deflationary narrative may erode investor confidence.
New wallet creation has also dropped sharply. On Sunday, only 86,539 new ETH addresses were created, the lowest this year.
This trend reflects declining speculative interest and reduced organic onboarding to the Ethereum network.
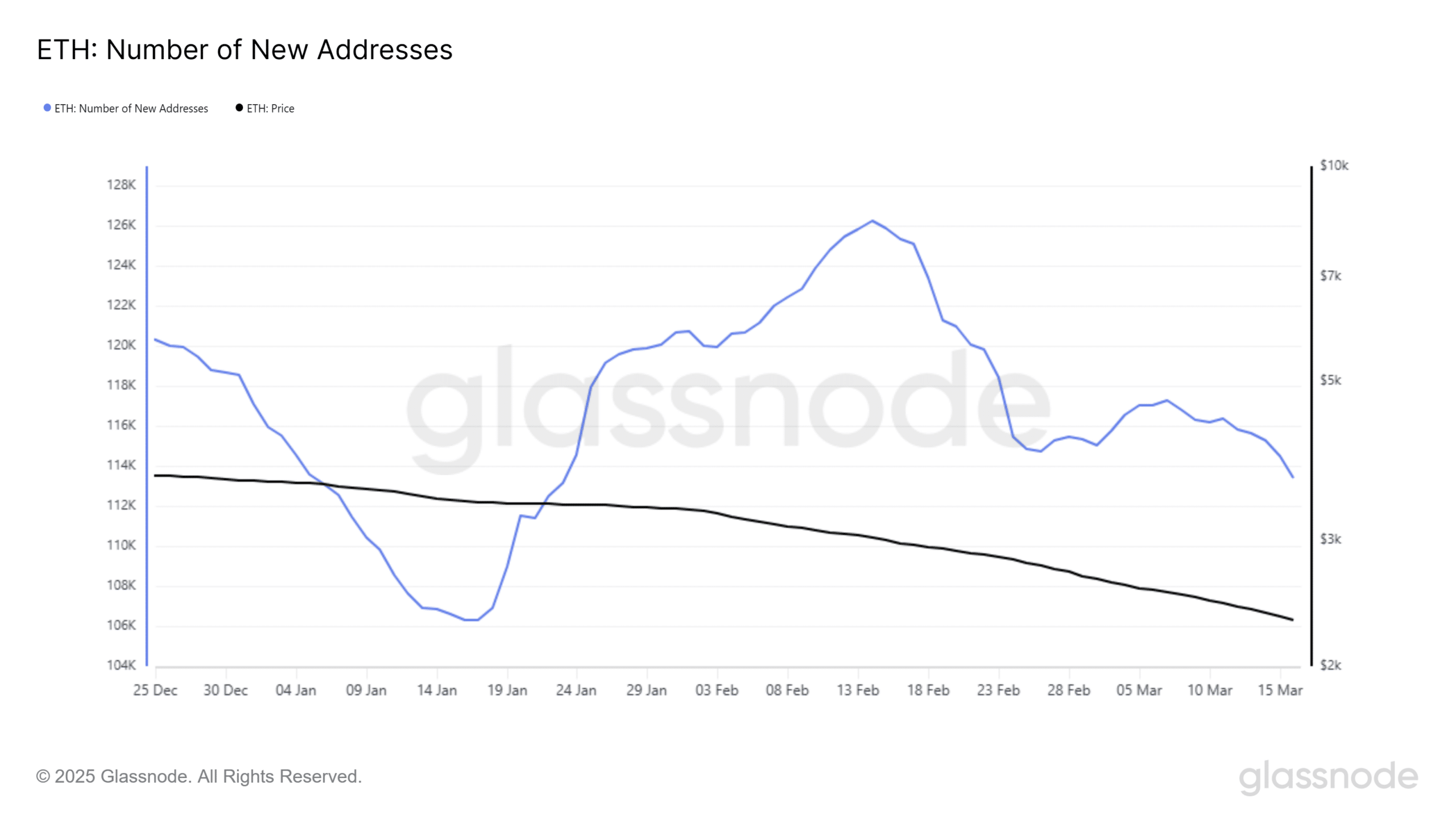

Source: Glassnode
Together, these on-chain metrics suggest a broader cooling in user appetite for Ethereum as concerns over inflation and alternative blockchain ecosystems continue to mount.
Impact on ETH’s supply
With on-chain activity declining, Ethereum’s supply is shifting toward inflation. Over the past month, over 71,000 ETH, worth $135 million, was added to the circulating supply, surpassing 120 million ETH.
The decrease in transactions has led to fewer fees being burned, weakening Ethereum’s deflationary mechanism. Without strong demand to counter the increased issuance, the surplus supply is creating consistent downward pressure on ETH’s price.
This trend is raising investor concerns about the network’s long-term value.


